
In the world of operating systems, Linux stands out as a cornerstone of the modern server landscape. Known for its versatility, robustness, and open-source nature, Linux powers millions of servers worldwide, forming the backbone of the internet and countless enterprise systems. In this article, we’ll explore what Linux is and dive into the most popular Linux distributions for server use.
What is Linux?

A Brief History of Linux
Linux traces its origins back to 1991, when Linus Torvalds, a Finnish computer science student, developed the Linux kernel as a free and open-source alternative to proprietary operating systems. Over the decades, Linux has grown into a powerful and highly customizable OS, supported by a vast global community of developers and organizations.
More Information Linux Click Hear
Core Components of Linux
At its core, Linux consists of three key components:
- Kernel: The kernel is the heart of Linux, managing hardware resources and enabling communication between hardware and software.
- Shell: The shell serves as the interface between the user and the system, allowing users to execute commands and scripts.
- User Space: This is where user applications and utilities reside, providing the tools to interact with the system.
Why Choose Linux for Servers?
Linux offers a host of advantages that make it a preferred choice for server environments:
- Security: Its open-source nature ensures rapid identification and patching of vulnerabilities. Additionally, Linux offers advanced permission and authentication mechanisms.
- Stability: Linux distributions are known for their reliability, often running for years without requiring a reboot.
- Flexibility: Whether you need a web server, database server, or cloud infrastructure, Linux can adapt to a wide range of workloads.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many Linux distributions are free, significantly reducing operational costs.
- Community Support: Linux boasts an active and knowledgeable community that provides extensive documentation, forums, and third-party tools.
Top Popular Linux Distributions for Servers
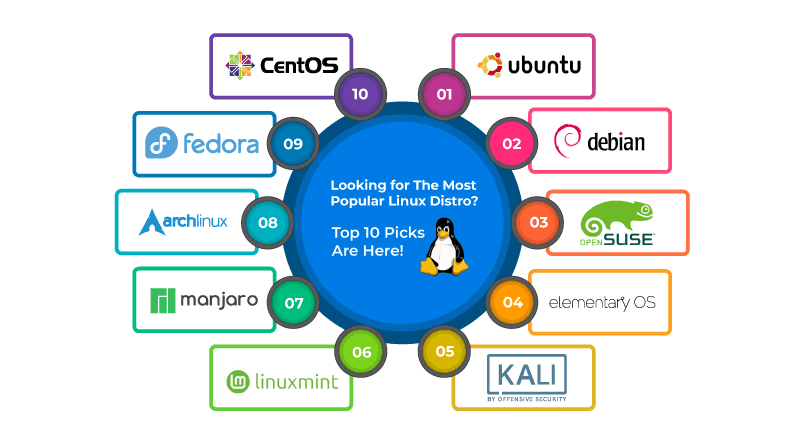
With dozens of Linux distributions available, choosing the right one for your server needs can be challenging. Here are some of the most popular and widely used Linux distributions for servers:
1. Ubuntu Server
Overview: Ubuntu Server is a user-friendly and versatile Linux distribution developed by Canonical. It is widely used in cloud computing and web hosting.
Strengths:
- Regular updates and long-term support (LTS) versions.
- Extensive community and commercial support.
- A vast library of pre-packaged software.
Common Use Cases:
- Web servers
- Cloud-based applications
- Development and testing environments
Key Features:
- Seamless integration with cloud platforms like AWS and Azure.
- Robust security features.
- Easy package management with APT.
2. CentOS/Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux
Overview: Following the discontinuation of CentOS, Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux have emerged as popular community-supported replacements, maintaining the same enterprise-grade reliability.
Strengths:
- Stability and long lifecycle.
- Compatibility with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
- Ideal for enterprise applications.
Common Use Cases:
- Enterprise-grade applications
- Database servers
- Virtualization hosts
Key Features:
- Focus on security and reliability.
- Robust SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) integration.
- Extensive support for enterprise tools.
3. Debian
Overview: Known for its stability and conservative approach to updates, Debian is a favorite for those seeking a secure and reliable server OS.
Strengths:
- Rigorous testing of software packages.
- Wide support across architectures.
- Strong emphasis on free software.
Common Use Cases:
- Web hosting
- Mail servers
- Network infrastructure
Key Features:
- APT package management system.
- High stability for mission-critical environments.
- Extensive software repositories.
4. Fedora Server
Overview: Fedora Server is a cutting-edge Linux distribution backed by Red Hat. It’s ideal for those who want to test the latest features and technologies.
Strengths:
- Access to the latest open-source innovations.
- Strong developer community.
- Integration with container technologies like Podman and Kubernetes.
Common Use Cases:
- Development environments
- Testing new software stacks
- Containerized applications
Key Features:
- Frequent updates and cutting-edge features.
- Modular approach for flexible software management.
- Excellent support for containerization.
5. SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES)
Overview: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is a commercially supported distribution designed for large-scale enterprise deployments.
Strengths:
- Comprehensive support and training services.
- Advanced tools for system management.
- Strong focus on security and compliance.
Common Use Cases:
- SAP workloads
- High-performance computing (HPC)
- Enterprise data centers
Key Features:
- Live kernel patching for minimal downtime.
- Integrated support for hybrid cloud environments.
- Advanced system monitoring tools.
6. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
Overview: A commercially supported distribution, RHEL is widely used in enterprise environments for its reliability and support.
Strengths:
- Extensive documentation and commercial support.
- Focus on enterprise stability and performance.
- Access to certified software stacks.
Common Use Cases:
- Mission-critical applications
- Cloud computing
- Middleware and database solutions
Key Features:
- Enterprise-grade support.
- Advanced security features.
- Tools for performance optimization.
What is Web Hosting? A Beginner’s Guide
FAQs About Linux and Server Administration
Q: What are the differences between Linux and Unix?
Linux is an open-source Unix-like operating system, while Unix is a proprietary system. Linux offers greater flexibility and community support.
Q: How do I choose the right Linux distribution for my server?
Consider your specific needs, such as stability, security, and support. For example, use Debian for stability or Fedora for cutting-edge features.
Q: Is Linux free to use?
Yes, most Linux distributions are free and open-source, though some, like RHEL and SLES, offer commercial versions with added support.
Q: How secure is Linux compared to other operating systems?
Linux is highly secure, thanks to its robust permission system and active community. Its open-source nature allows for quick vulnerability fixes.
Conclusion
Linux is a versatile and powerful operating system that has become the backbone of modern server infrastructure. With its numerous advantages—security, stability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness—it’s no wonder Linux dominates the server market. By understanding the unique strengths of popular distributions like Ubuntu Server, CentOS, Debian, Fedora, and SUSE, you can choose the perfect Linux solution for your specific needs.
Start exploring Linux today to unlock its full potential for your server needs. Whether you’re a system administrator, developer, or IT professional, Linux offers tools and resources to help you succeed.






Comments
lovart
Lovart AI Agent is a game-changer for designers who want to blend creativity with AI efficiency. The tri-modal interaction makes the design process feel intuitive and smart. Can’t wait to see it evolve! Lovart AI Agent
lovart
Lovart AI is a game-changer for designers who want speed without sacrificing creativity. Its tri-modal interface and AI-powered canvas make refining ideas smoother than ever. Definitely worth the wait! Lovart AI is setting a new standard.